Inside China’s Dark Factories: How AI-Powered Automation Is Reshaping Global Manufacturing
- GordonGekko

- Apr 13, 2025
- 2 min read
Updated: Apr 15, 2025
Imagine a factory that runs 24/7, doesn't need lights, and doesn't employ a single worker. Welcome to the era of dark factories—China’s bold leap into fully automated, human-free manufacturing.
Once the world’s manufacturing powerhouse due to low labour costs, China is now reinventing itself through robotics, artificial intelligence, and big data. The goal? Stay competitive as wages rise, reduce energy consumption, and dominate the future of industrial production.
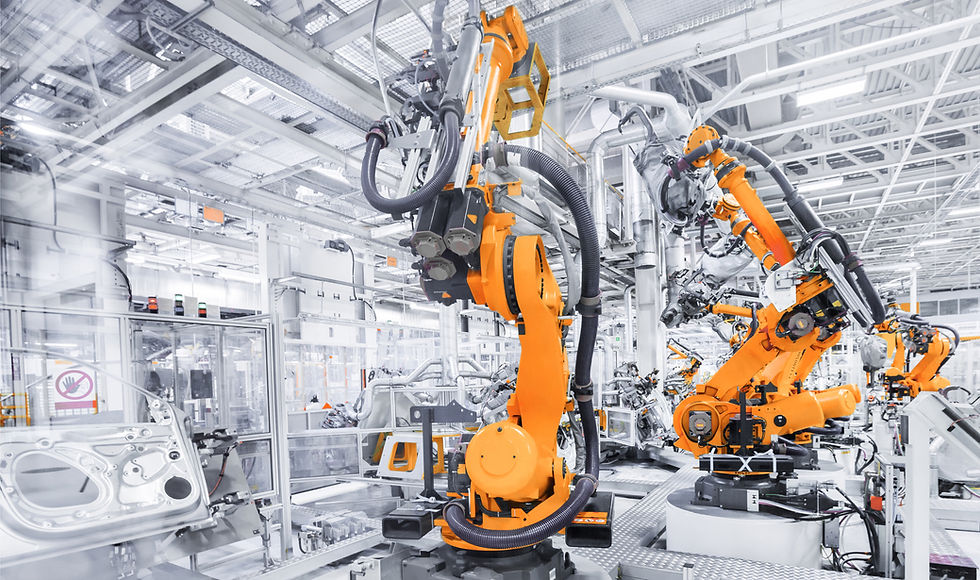
🔧 What Is a Dark Factory?
A dark factory is an entirely automated production facility designed to run without any human workers on site. With no need for lighting, air conditioning, or human break rooms, these factories are optimized for speed, efficiency, and cost.
Core technologies powering dark factories include:
Robotics and robotic arms
AI and machine vision
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
Digital twins and real-time analytics
🏭 Real-World Examples in China
China has been quick to roll out dark factories across various sectors. Some of the most notable developments include:
🔹 Xiaomi Smart Factory (Beijing)
100% automated production line
Produces up to 10 million smartphones annually
Real-time AI monitors and adjusts the production process
Minimal human supervision—mostly engineers managing systems off-site
🔹 Geely's Xi’an Plant
Known as the "Black Light Factory"
Uses over 1,000 intelligent robots
Fully integrated smart system for real-time coordination across stages like stamping, welding, painting, and assembly
🔹 DJI Drone Manufacturing (Shenzhen)
High automation in component assembly and packaging
Reduced production lead times from days to hours
⚡ Why China Is Embracing Dark Factories
The move towards dark factories is driven by several strategic priorities:
Labor Cost Pressure: Rising wages have eroded China’s traditional low-cost advantage.
Global Competitiveness: As Southeast Asia and India offer cheaper labor, automation gives China a technological edge.
Energy and Environmental Efficiency: No lighting or climate control reduces industrial energy usage by 15–20%.
"Made in China 2025" Strategy: This policy promotes innovation in smart manufacturing and aims to upgrade China’s industrial base.
🌍 Global Ripple Effects
China’s dark factory revolution is sending shockwaves across the world:
Job Displacement: Labor-intensive industries in ASEAN countries like Indonesia, Vietnam, and Thailand face increased competition from cheap, automated Chinese goods.
Supply Chain Shifts: Companies are being forced to rethink sourcing strategies. Some are nearshoring to ASEAN, while others invest in their own automation.
Dumping Risk: Overproduction from dark factories may lead to surplus goods being dumped in foreign markets, triggering trade tensions.
🧠 The Future of Work and Automation
Dark factories signal not just a shift in technology, but a transformation of the global labor model. As machines take over repetitive tasks, countries must retrain workers, invest in STEM education, and pivot toward higher-value roles in design, programming, and maintenance.
🧭 Final Thoughts
China’s dark factories aren’t just factories—they’re the future of industrialization. By blending AI, robotics, and real-time data, China is rewriting the playbook on how products are made.
For other nations and industries, the message is clear: adapt, automate, or fall behind.


